

Open virt-manager
virt-manager. Launch the application from the menu and submenu. Alternatively, run the virt-manager command as root.
Select the hypervisor
qemu.
Start the new virtual machine wizard
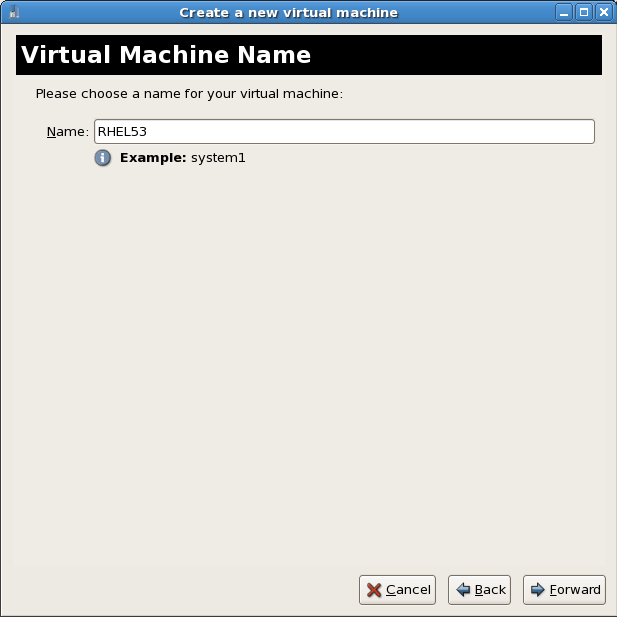
Name the virtual machine
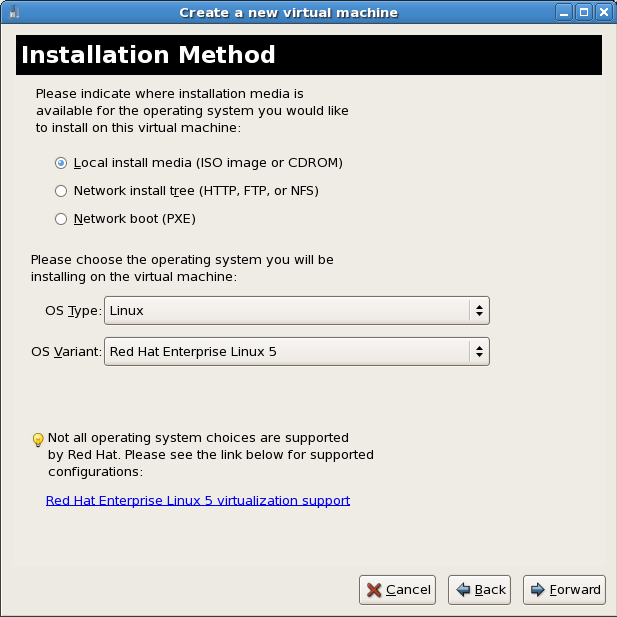
Choose a virtualization method

Select the installation method
Locate installation media
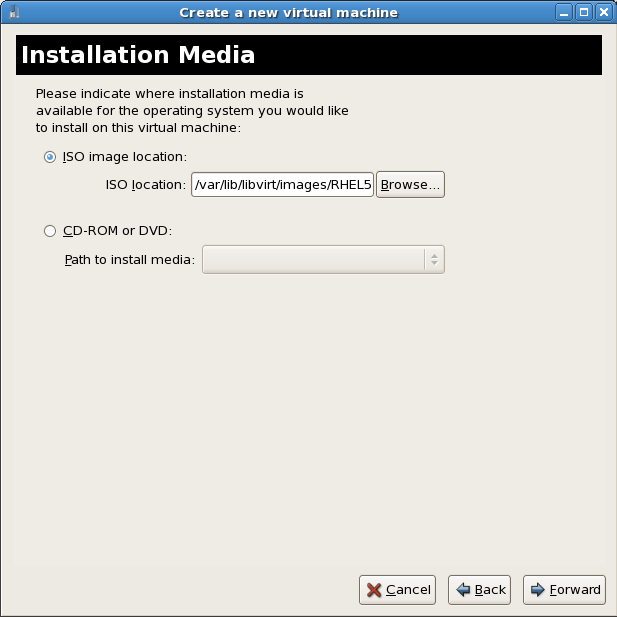
/var/lib/libvirt/images/. Cualquier otra ubicación puede necesitar una configuración adicional de SELinux, consulte los detalles en Sección 7.1, “SELinux y virtualización completas”.
Storage setup
/var/lib/libvirt/images/. Asigne el almacenamiento suficiente para su huésped virtualizado. Asigne espacio suficiente para su huésped virtualizado y cualquier aplicación que se requiera
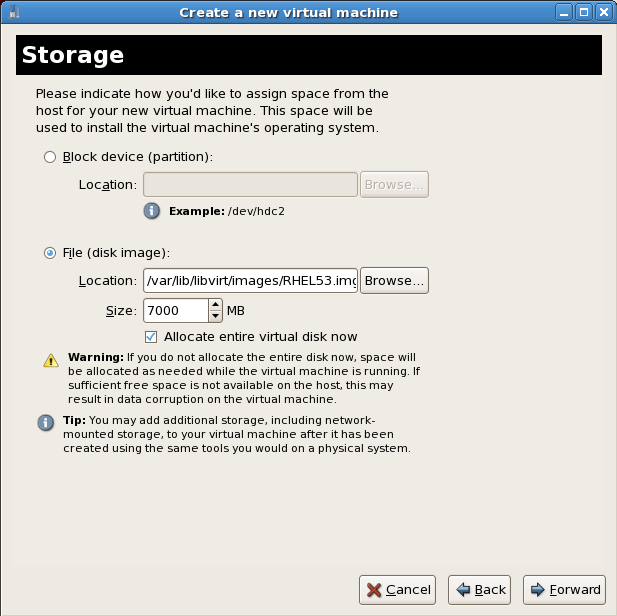
Network setup
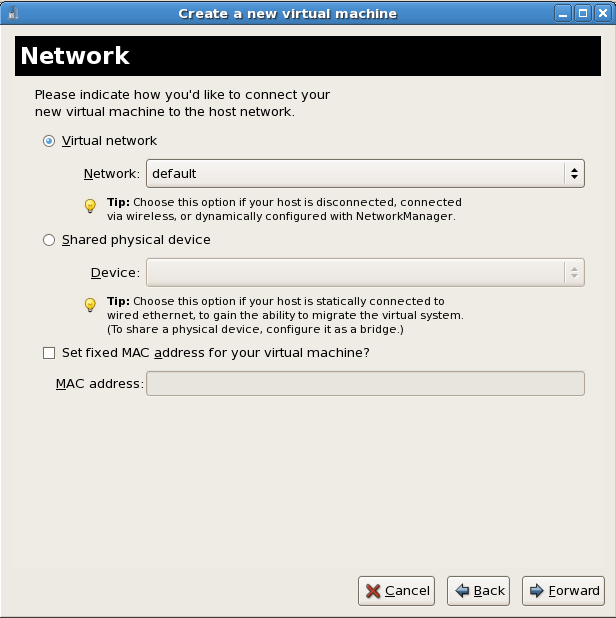
Memory and CPU allocation
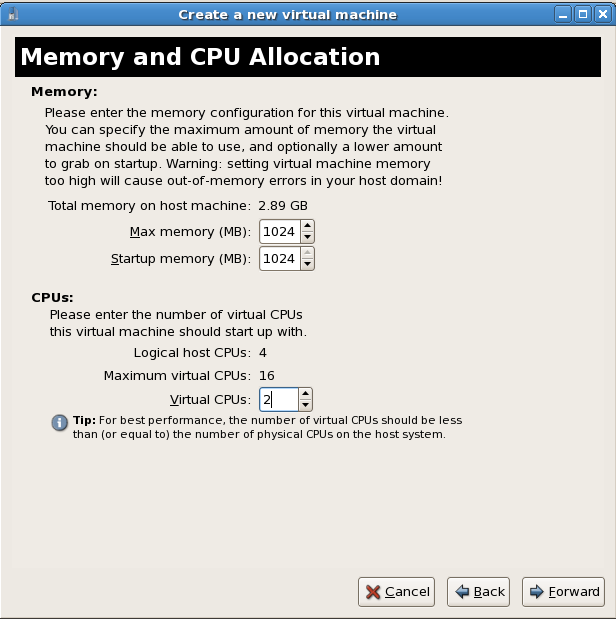
Verify and start guest installation
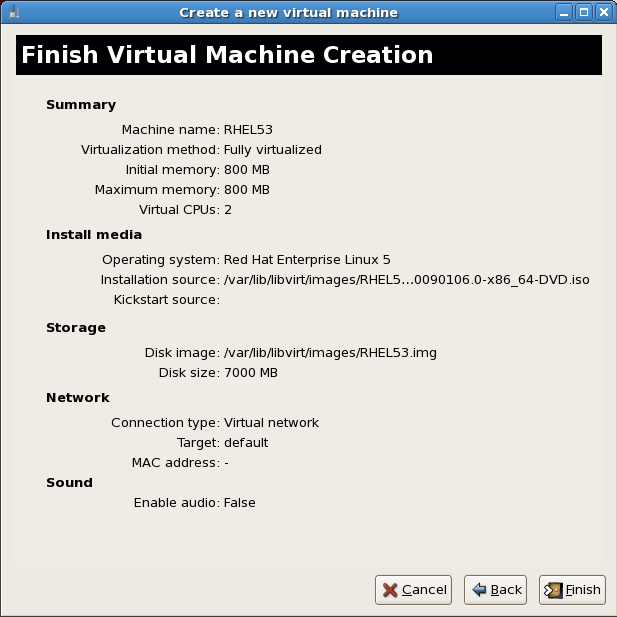
Instalación de Linux