Chapter 7. Troubleshooting
The following chapter describes what happens when SELinux denies access; the top three causes of problems; where to find information about correct labeling; analyzing SELinux denials; and creating custom policy modules with audit2allow.
7.1. What Happens when Access is Denied
SELinux decisions, such as allowing or disallowing access, are cached. This cache is known as the Access Vector Cache (AVC). Denial messages are logged when SELinux denies access. These denials are also know as "AVC denials", and are logged to a different location, depending on which daemons are running:
| Daemon | Log Location |
|---|
| auditd on | /var/log/audit/audit.log |
| auditd off; rsyslogd on | /var/log/messages |
| setroubleshootd, rsyslogd, and auditd on | /var/log/audit/audit.log. Easier-to-read denial messages also sent to /var/log/messages |
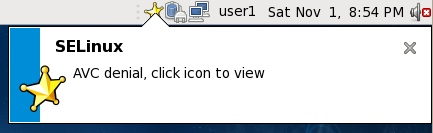
If you are running the X Window System, have the setroubleshoot and setroubleshoot-server packages installed, and the setroubleshootd and auditd daemons are running, a yellow star and a warning are displayed when access is denied by SELinux:
Clicking on the star presents a detailed analysis of why SELinux denied access, and a possible solution for allowing access. If you are not running the X Window System, it is less obvious when access is denied by SELinux. For example, users browsing your website may receive an error similar to the following:
Forbidden
You don't have permission to access file name on this server
For these situations, if DAC rules (standard Linux permissions) allow access, check /var/log/messages and /var/log/audit/audit.log for "SELinux is preventing" and "denied" errors respectively. This can be done by running the following commands as the Linux root user:
grep "SELinux is preventing" /var/log/messages
grep "denied" /var/log/audit/audit.log