7.3.2. Searching For and Viewing Denials
This section assumes the setroubleshoot, setroubleshoot-server, and audit packages are installed, and that the auditd, rsyslogd, and setroubleshootd daemons are running. Refer to Section 5.2, “Which Log File is Used” for information about starting these daemons. A number of tools are available for searching for and viewing SELinux denials, such as ausearch, aureport, and sealert.
ausearch
The audit package providesausearch. From the ausearch(8) manual page: "ausearch is a tool that can query the audit daemon logs based for events based on different search criteria"[16]. The ausearch tool accesses /var/log/audit/audit.log, and as such, must be run as the Linux root user:
| Searching For | Command |
|---|---|
| all denials | /sbin/ausearch -m avc |
| denials for that today | /sbin/ausearch -m avc -ts today |
| denials from the last 10 minutes | /sbin/ausearch -m avc -ts recent |
To search for SELinux denials for a particular service, use the -c option, where comm-namecomm-name "is the executable’s name"[17], for example, httpd for the Apache HTTP Server, and smbd for Samba:
/sbin/ausearch -m avc -c httpd
/sbin/ausearch -m avc -c smbd
Refer to the ausearch(8) manual page for further ausearch options.
aureport
The audit package providesaureport. From the aureport(8) manual page: "aureport is a tool that produces summary reports of the audit system logs"[18]. The aureport tool accesses /var/log/audit/audit.log, and as such, must be run as the Linux root user. To view a list of SELinux denials and how often each one occurred, run the aureport -a command. The following is example output that includes two denials:
# /sbin/aureport -a AVC Report ======================================================== # date time comm subj syscall class permission obj event ======================================================== 1. 11/01/2008 21:41:39 httpd unconfined_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 195 file getattr system_u:object_r:samba_share_t:s0 denied 2 2. 11/03/2008 22:00:25 vsftpd unconfined_u:system_r:ftpd_t:s0 5 file read unconfined_u:object_r:cifs_t:s0 denied 4
sealert
The setroubleshoot-server package providessealert, which reads denial messages translated by setroubleshoot-server. Denials are assigned IDs, as seen in /var/log/messages. The following is an example denial from messages:
setroubleshoot: SELinux is preventing httpd (httpd_t) "getattr" to /var/www/html/file1 (samba_share_t). For complete SELinux messages. run sealert -l 84e0b04d-d0ad-4347-8317-22e74f6cd020
In this example, the denial ID is 84e0b04d-d0ad-4347-8317-22e74f6cd020. The -l option takes an ID as an argument. Running the sealert -l 84e0b04d-d0ad-4347-8317-22e74f6cd020 command presents a detailed analysis of why SELinux denied access, and a possible solution for allowing access.
If you are running the X Window System, have the setroubleshoot and setroubleshoot-server packages installed, and the setroubleshootd daemon running, a yellow star and a warning are displayed when access is denied by SELinux. Clicking on the star launches the sealert GUI, and displays denials in HTML output:
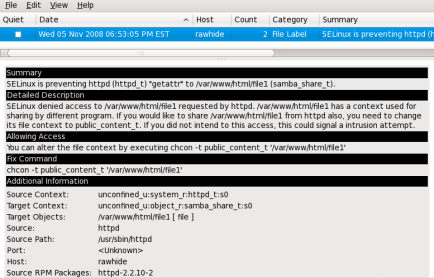
Run the
sealert -bcommand to launch thesealertGUI.Run the
sealert -l \*command to view a detailed anaylsis of all denials.As the Linux root user, run the
sealert -a /var/log/audit/audit.log -H > audit.htmlcommand to create a HTML version of thesealertanalysis, as seen with thesealertGUI.