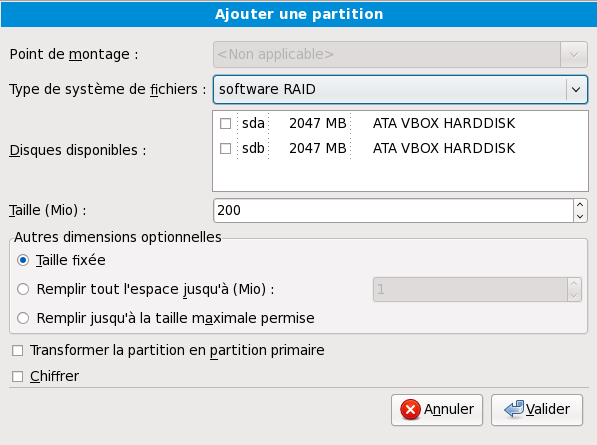
New: Select this option to add a partition or LVM physical volume to the disk. In the Add partition dialog, choose a mount point and a partition type. If you have more than one disk on the system, choose which disks the partition may inhabit. Indicate a size in megabytes for the partition. If you wish to encrypt the partition, select that option.
Illegal Partitions
You cannot create separate partitions for the
/bin/,
/dev/,
/etc/,
/lib/,
/proc/,
/root/, and
/sbin/ directories. These directories must reside on the
/ (root) partition.
The /boot partition may not reside on an LVM volume group. Create the /boot partition before configuring any volume groups. Furthermore, you cannot use the ext4 or btrfs filesystems for the /boot partition.
Avoid placing /usr on a separate partition. If /usr does not reside on the / (root) partition, the boot process becomes more complex and some systems (for example, those with iSCSI storage) will fail to boot.
You may also choose from three options for sizing your partition:
- Fixed size
Use a fixed size as close to your entry as possible.
- Fill all space up to
Grow the partition to a maximum size of your choice.
- Fill to maximum allowable size
Grow the partition until it fills the remainder of the selected disks.
Partition Sizes
The actual partition on the disk may be slightly smaller or larger than your choice. Disk geometry issues cause this effect, not an error or bug.
Select the Encrypt partition option to encrypt all information on the disk partition.
After you enter the details for your partition, select
OK to continue. If you chose to encrypt the partition, the installer prompts you to assign a passphrase by typing it twice. For hints on using good passphrases, refer to
Section 7.17, « Set the Root Password ».
Editer : utilisé pour modifier les attributs de la partition actuellement sélectionnée dans la section Partitions. Lorsque vous sélectionnez Editer, une boîte de dialogue s'ouvre. Une partie ou la totalité des champs peuvent être modifiés, selon que les informations sur la partition aient déjà été enregistrées sur le disque ou non.
Vous pouvez également modifier l'espace libre disponible représenté dans l'affichage graphique afin de créer une nouvelle partition. Mettez en surbrillance l'espace libre et sélectionnez le bouton Editer ou double-cliquez sur l'espace libre pour le modifier.
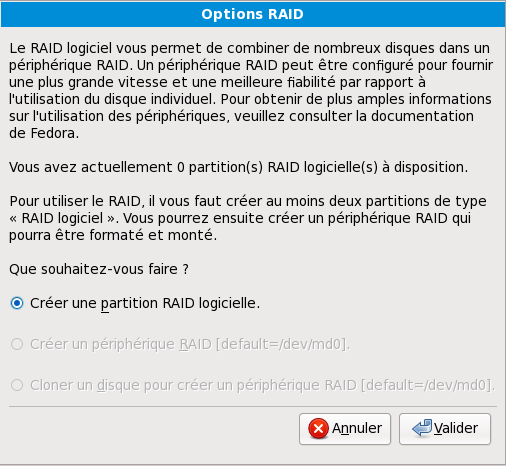
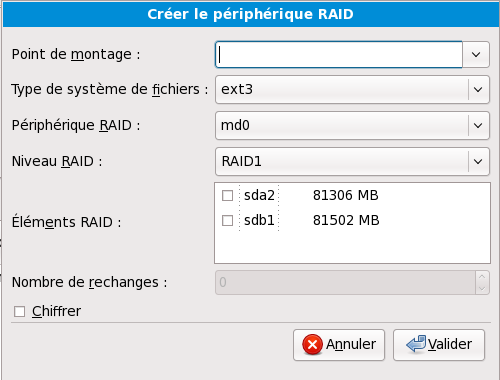
Pour créer un périphérique RAID, vous devez d'abord créer des partitions RAID logicielles (ou réutiliser des partitions existantes). Après avoir créé plusieurs partitions RAID logicielles, sélectionnez RAID afin de lier les partitions RAID logicielles à un périphérique RAID.
Effacer : utilisé pour supprimer la partition actuellement sélectionnée dans la section Partition du disque en cours. Vous serez invité à confirmer la suppression de toute partition.
To delete an LVM physical volume, first delete any volume groups of which that physical volume is a member.
If you make a mistake, use the Reset option to abandon all the changes you have made.
Reset: Used to restore the partitioning screen to its original state. All changes made will be lost if you Reset the partitions.
RAID: Used to provide redundancy to any or all disk partitions. It should only be used if you have experience using RAID.
Pour créer un périphérique RAID, vous devez d'abord créer des partitions RAID logicielles. Après avoir créé plusieurs partitions RAID logicielles, sélectionnez RAID afin de lier les partitions RAID logicielles à un périphérique RAID.
- Create a software RAID partition
Choose this option to add a partition for software RAID. This option is the only choice available if your disk contains no software RAID partitions.
- Create a RAID device
Choose this option to construct a RAID device from two or more existing software RAID partitions. This option is available if two or more software RAID partitions have been configured.
- Clone a drive to create a RAID device
Choose this option to set up a RAID mirror of an existing disk. This option is available if two or more disks are attached to the system.
LVM: Allows you to create an LVM logical volume. The role of LVM (Logical Volume Manager) is to present a simple logical view of underlying physical storage space, such as a hard drive(s). LVM manages individual physical disks — or to be more precise, the individual partitions present on them. It should only be used if you have experience using LVM. Note, LVM is only available in the graphical installation program.
To assign one or more physical volumes to a volume group, first name the volume group. Then select the physical volumes to be used in the volume group. Finally, configure logical volumes on any volume groups using the Add, Edit and Delete options.
You may not remove a physical volume from a volume group if doing so would leave insufficient space for that group's logical volumes. Take for example a volume group made up of two 5 GB LVM physical volume partitions, which contains an 8 GB logical volume. The installer would not allow you to remove either of the component physical volumes, since that would leave only 5 GB in the group for an 8 GB logical volume. If you reduce the total size of any logical volumes appropriately, you may then remove a physical volume from the volume group. In the example, reducing the size of the logical volume to 4 GB would allow you to remove one of the 5 GB physical volumes.
LVM Unavailable in Text Installs
LVM initial set up is not available in a text-mode installation. The installer allows you to edit pre-configured LVM volumes. If you need to create an LVM configuration from scratch, hit Alt+F2 to use the terminal, and run the lvm command. To return to the text-mode installation, hit Alt+F1.