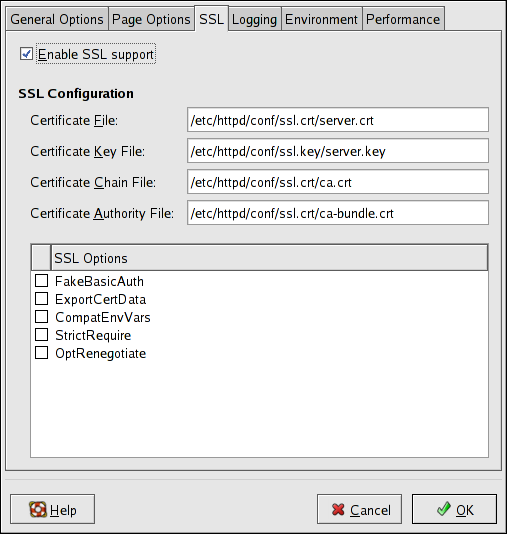
The mod_ssl enables encryption of the HTTP protocol over SSL. SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) protocol is used for communication and encryption over TCP/IP networks. The SSL tab enables you to configure SSL for your server. To configure SSL you need to provide the path to your:
Certificate file - equivalent to using the SSLCertificateFile directive which points the path to the PEM (Privacy Enhanced Mail)-encoded server certificate file.
Key file - equivalent to using the SSLCertificateKeyFile directive which points the path to the PEM-encoded server private key file.
Certificate chain file - equivalent to using the SSLCertificateChainFile directive which points the path to the certificate file containing all the server's chain of certificates.
Certificate authority file - is an encrypted file used to confirm the authenticity or identity of parties communicating with the server.
FakeBasicAuth - enables standard authentication methods used by Apache. This means that the Client X509 certificate's Subject Distinguished Name (DN) is translated into a basic HTTP username.
ExportCertData - creates CGI environment variables in SSL_SERVER_CERT, SSL_CLIENT_CERT and SSL_CLIENT_CERT_CHAIN_n where n is a number 0,1,2,3,4... These files are used for more certificate checks by CGI scripts.
CompatEnvVars - enables backward compatibility for Apache SSL by adding CGI environment variables.
StrictRequire - enables strict access which forces denial of access whenever the SSLRequireSSL and SSLRequire directives indicate access is forbiden.
OptRenegotiate - enables avoidance of unnecessary handshakes by mod_ssl which also performs safe parameter checks. It is recommended to enable OptRenegotiate on a per directory basis.