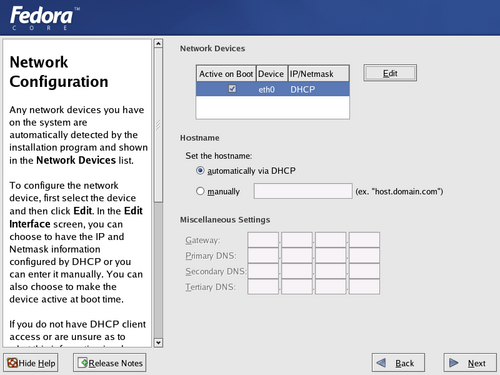
Use this screen to customize the network settings of your Fedora system.
You may not need to manually configure these settings if your computer is part of an existing network, or if it is a laptop that moves between networks. By default, Fedora Core activates all of the network interfaces on your computer and configures them to use DHCP, or Dynamic Host Control Protocol. Most networks have a DHCP service that automatically supplies connected systems with configuration data.
Wireless interfaces using DHCP will join an open wireless network once it is in range. Many wireless networks are restricted, and only accept systems which have the correct security credentials.
Fedora displays a list of network interfaces detected on your computer. Each interface must have a unique IP address on the network to which it is attached. The interface may receive this address from the network DHCP service.
To manually assign an IP address, highlight the interface on the Network Device list and select Edit. Fedora then displays a network configuration dialog. Deselect the Configure using DHCP checkbox, so that it is empty. Enter the IP Address and the appropriate Netmask for the interface. Then select OK.
If your computer will be acting as a server, do not use DHCP. Manually configure networking instead. A manual network configuration assures that your server will join the local network even if the DHCP provider is down.
Specify whether an interface should be automatically activated at boot time with the Active on Boot checkbox for that device. You may manually activate a network interfaces at any time after the system has booted.
![[Note]](./stylesheet-images/note.png) | Modem Configuration |
|---|---|
The Network Configuration screen does not list modems. Configure these devices after installation with either the Internet Configuration Wizard or Network Cnfiguration utility to set up Internet access on your Fedora system. The settings for your modem are specific to your particular Internet Service Provider (ISP). | |